Table of Contents
What Are Sebaceous Glands?
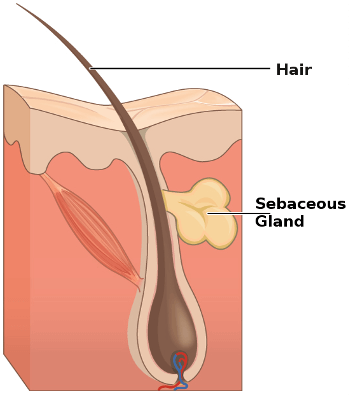 Sebaceous glands are tissues in our bodies which secrete sebum. Sebum is a wax-like oil that is secreted in your hair follicles. Sebum is made up of various fats such as triglycerides, cholesterol, squalene and wax esters.
Sebaceous glands are tissues in our bodies which secrete sebum. Sebum is a wax-like oil that is secreted in your hair follicles. Sebum is made up of various fats such as triglycerides, cholesterol, squalene and wax esters.
Location of Sebaceous Glands
Sebaceous glands can be found on all parts of your skin apart from your bottom lip, palms, and soles of your feet.
Types of Sebaceous Glands
There are two main types of sebaceous glands; those which connect to your hair follicles, and those which do not. Sebaceous glands which are connected to the hair follicles deposit sebum on your hair.
Sebaceous Gland Development
We have the same number of sebaceous glands for life, but their size tends to increase as we age.
Sebaceous gland formation begins during the fourth month of gestation and continues to early life. When we are born, the clear, waxy substance that covers our skin right after birth is from our sebaceous glands. After being born, our sebaceous glands shrink.
At around age six, our sebaceous glands start to expand ultimately reaching peak activity at puberty. The activity of the sebaceous glands is primarily controlled by testosterone.
Function of Sebaceous Glands
The primary function of your sebaceous glands is to secrete sebum which lubricates your skin, thus preventing moisture loss. This helps your skin remain pliable. Without sebum, your skin would become dry and crack easily. Cracks are more likely to get infected since bacteria and viruses can get through broken skin.
The function of sebum in our hair is to waterproof our hair. Without sebum, our hair would become brittle and dry.
Sebaceous Gland Problems
Low functioning sebaceous glands cause our skin to break and infections to occur. Over functioning sebaceous glands cause acne. We get pimples when a sebaceous gland clogs, causing sebum to accumulate in the follicles. This excess sebum causes bacteria to grow. The breakdown of triglycerides in the sebum by bacteria causes the release of fatty acids. This triggers inflammatory lesions, also known as pimples.
Over functioning sebaceous glands also cause cysts, which are painful pockets of pus that occur within the sebaceous ducts when they get blocked. Acne tends to be closer to your skin surface, while cysts tend to be further down in the skin and are painful when touched because they are close to the nerves in your skin. Over functioning sebaceous glands also cause hyperplasia and sebaceous adenoma. Hyperplasia is the rapid growth of tissue that can lead to cancer. Sebaceous adenomas are masses of cells in the sebaceous duct that can be a sign of cancer.
